
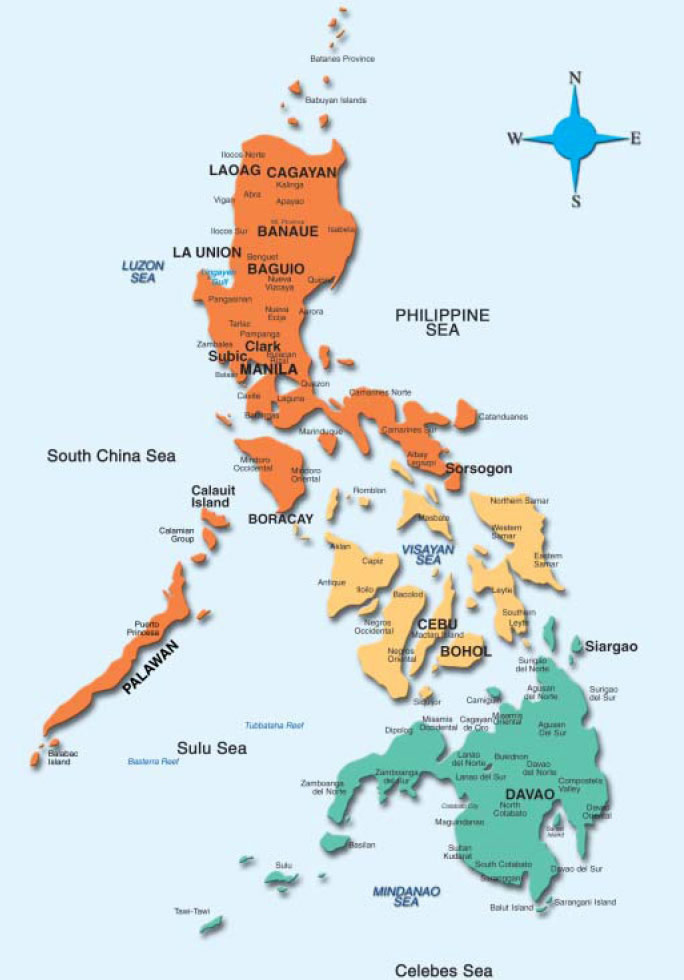
The Republic of the Philippines is an archipelago of 7,107 islands lying on the western rim of the Pacific Ocean and north of the equator.
The northern part of the country is separated from Taiwan by the Bashi Channel. It is bounded on the east by the Philippine Sea, on the south by the Celebes Sea, and on the west by the South China Sea.
It is approximately 6,290 kilometers away from Australia or, in terms of travel time, seven hours by plane from Sydney to Manila, the capital city of the Philippines.
The total land area is about 298,170 square kilometers (114,830 square miles).
The Philippines is composed of three major islands known as Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao. The largest island is Luzon, followed by Mindanao and the Visayas group. The Visayan region is composed of about 6,000 islands, including Panay, Samar, Cebu, Leyte and Bohol. Mindanao encompasses about 400 islands.
The islands extend about 1,850 kilometers from north to south and almost 1,127 kilometers from east to west. The coastlines of all the islands are extremely irregular, measuring about 36,289 kilometers in length.
Of volcanic origin, the Philippines is generally mountainous. Mountain ranges extend north to south, running parallel to the coasts and, in many places, bordering them.
The mountains in Luzon include the Sierra Madre, Cordillera Central, the Caraballo Mountains and the Zambales Mountains. In the second largest island, Mindanao, are the Diwata Mountains and the mountain ranges in southern Mindanao including Mount Apo (a volcano) which, at 2,954 meters, is the highest point in the Philippines.
Seismic disturbances are often experienced in the islands that include 20 active volcanoes. The most recent volcanic eruptions were in 1993 (Mayon Volcano in the Bicol Region, southeastern Luzon, dormant for 600 years) and in June 1991 and July 1992 (Mount Pinatubo, central Luzon).
The larger islands have a more diversified topography, with rivers, broad plains and level, fertile valleys in the interior. Luzon has the Cagayan Valley (a plain about 80 kilometers wide, the Central Plain (extending from Lingayen Gulf to Manila Bay), the Cagayan River (longest river in Luzon), Abra River, Chico River, the large Laguna de Bay, Agno River, Pampanga River and Bicol River. Mindanao contains the Mindanao Valley (the largest lowland area), the Agusan River the Rio Grande de Mindanao (known in its upper course as the Pulangi).
The Philippines lies within the tropics and has a mean annual temperature of about 27ºC. Rainfall averages 2030 millimeters per year in the lowlands. On most islands of the Philippines, the rain season occurs during the summer monsoon, from May to November, when the wind blows from the southwest; the dry season occurs during the winter monsoon, from December to April, when the wind blows from the northeast. From June to October, typhoons sometimes appear in the Philippines.
The Philippines contains about 19 percent arable land and 46 percent forests and woodlands. Aside from being endowed with forest resources it has also rich deposits of minerals, principally gold, copper, iron, chromite, manganese, salt and coal. Other minerals are silver, lead, mercury, limestone, petroleum, nickel and uranium.
Mangrove trees and nipa palms grow in coastal swamps and coarse grasses cover many areas of the uplands. The forests contain trees such as banyan, palm trees, rubber trees and indigenous hard wood trees such as the apitong, yakal, lauan, camagong, ipil, narra, and mayapis. Bamboo, clove, and pepper plants grow in the wild, as do numerous species of orchid. Abaca or Manila hemp yields the fibrous material for making cordage, textiles, and hats.
The most important animal species include the domesticated water buffalo called the carabao, several species of deer, wild and domesticated pigs, the mongoose, and a variety of humped cattle. Reptiles are numerous, and the islands contain about 760 species of birds, including colorful parrots. Coastal waters teem with marine fauna, particularly mollusks, for which the Philippines is noted. Pearl oysters are harvested in Sulu Archipelago from which are extracted the famous lustrous Sulu pearls.
Manila, the capital city, is the country's chief port and main commercial center.
The last official census in 1990 showed that Manila proper had a population 1,601,234, while the greater metropolitan area had 7,948,398. Quezon City, which forms part of the Manila metropolitan area, holds a population of 1,669,776, and served as the country's capital from 1948 to 1976. Davao, a provincial capital and seaport, contains 843,607 people. Cebu, a seaport and trade center for the agricultural and coal-mining industries, has 610,417 people. Zamboanga, also a seaport has 442,000.